Difference between revisions of "Filtering scope"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
! style="font-weight: bold;" | Averaged buffer | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | Averaged buffer | ||
! style="font-weight: bold;" | FFT | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | FFT | ||
| − | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | lienear corelation/regression | + | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | lienear corelation / regression |
! style="font-weight: bold;" | Combine Conditions | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | Combine Conditions | ||
! style="font-weight: bold;" | ERP | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | ERP | ||
! style="font-weight: bold;" | Coherence | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | Coherence | ||
| − | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | Time Frequency plot (single click) | + | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | Time Frequency plot<br>(single click) |
! style="font-weight: bold;" | TopViewer | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | TopViewer | ||
! style="font-weight: bold;" | Source Analysis | ! style="font-weight: bold;" | Source Analysis | ||
Revision as of 18:17, 2 February 2021
| Module information | |
| Modules | BESA Research |
| Version | 6.1 or higher |
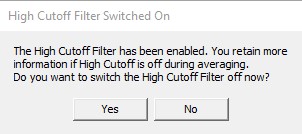
In EEG/MEG data analysis frequency filtration is one of the most basic and at the same time important operations. In BESA Research filtration is implemented as a linear operation so it is interchangeable in the processing pipeline - it can be changed at every processing step in almost all situations. There are however some moments that filtration cannot be applied in a linear manner - i.e. averaging. In general, we recommend not apply filtration during such types of operations as it can be replied afterward. You will be prompted by the application if you encounter such a moment in data analysis:
Also at some stages of the data processing, the filtration is of major importance, therefore we made it more accessible and you can easily redefine it. Please have a look at the table below:
| Filter type | Review window | Search Average View | Averaged buffer | FFT | lienear corelation / regression | Combine Conditions | ERP | Coherence | Time Frequency plot (single click) |
TopViewer | Source Analysis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low/High pass | Main | Main / can be redefine to default values(2-35Hz) | as used during buffer creation | Main | Main | None | ERP | ERP | Main | Main | SA |
| Notch | Main | Main / can be redefine to default values(2-35Hz) | as used during buffer creation | Main | Main | None | Main | Main | Main | Main | Main |
| Bandpass | Main | Main / can be redefine to default values(2-35Hz) | as used during buffer creation | Main | Main | None | ERP | ERP | Main | Main | Main |
| Polygraphic | Main* | Main* / can be redefine to default values(2-35Hz) | as used during buffer creation | Main* | Main* | None | Main* | Main* | Main* | Main* | n.a. |
| artifact correction | Main | Main / can be redefine to default values(2-35Hz) | as used during buffer creation | Main | Main | Main | ERP | ERP | Main | Main | Main/SA |
Contents
Main settings
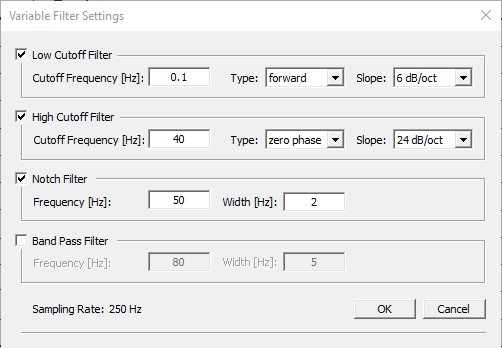
The main setting for artifact correction can be set using EdF or menu entry Filters/Edit Filter Settings...
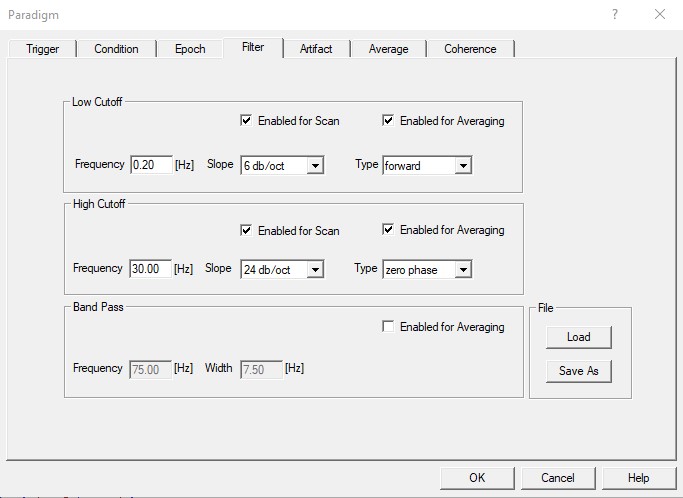
Specific ERP settings
The ERP filter settings can be set during paradigm definition. Note that there are two different settings - for artifact scan and for averaging
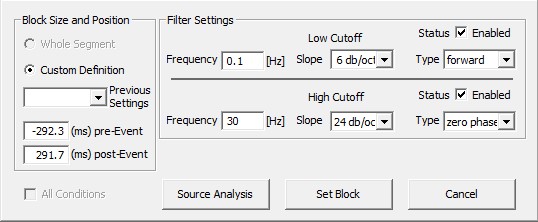
Specific Source Analysis settings
For source analysis (SA), if you press 'ESI/MSI button on the toolbar ribbon Main filter settings will be used.) Filters for SA can be set during sending a block of data to Source Analysis (right-click on the highlighted block and select Source Analysis).
Notch filter
Note that because of its generic nature - power line artifact removal - notch filter is treated differently. The notch filter value populates from Main setting to all subsequent applications.
Bandpass filter
Bandpass filter is complementary to high/low pass filter combination. For convenience, it is treated differently and also populates to all subsequent applications from Main setting.
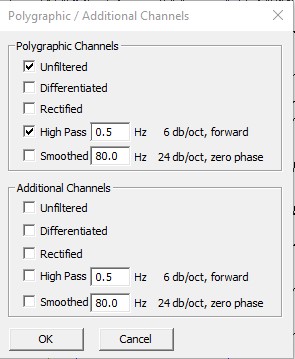
Polygraphic filter
Polygraphic channels are filtered using Main settings. Note that there are additional settings that can be applied to the polygraphic filter accessible via Filters/Polygraphic/Additional Chans...