Difference between revisions of "Talairach Transformation File"
(Created page with "{{BESAInfobox |title = Module information |module = BESA Research Basic or higher |version = 5.2 or higher }} The tal file contains the transformation parameters from AC-PC c...") |
|||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
Distance AC to LP 68 | Distance AC to LP 68 | ||
</source > | </source > | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Talairach values.png|600px]] | ||
| + | |||
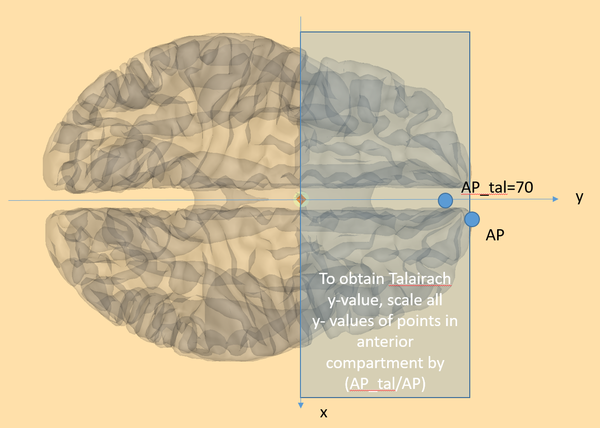
| + | Example of how to apply Talairach values. The principle is followed in all three directions (x, y, z). First the compartment is identified (e.g. for z axis, superior to AC, or inferior to AC). Then the coordinate is scaled with the Talairach value divided by the real value. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For the posterior compartments (y-axis), it is slightly more complicated because there are two posterior compartments: Between AC and PC, and between PC and PP. Once it is decided which compartment is the correct one, the scaling is done for this compartment only; e.g. if the compartment is between PC and PP: | ||
| + | First subtract the relevant points from the value, i.e. |y|’ = |y|-PC. Then, scale y’ with (PP_tal-PC_tal)/(PP-PC). Then add PC_tal. Done! | ||
Revision as of 18:09, 28 November 2017
| Module information | |
| Modules | BESA Research Basic or higher |
| Version | 5.2 or higher |
The tal file contains the transformation parameters from AC-PC coordinate system to the Talairach coordinate system. The following seven points are listed:
- Item 1 AP: Distance from x-z-plane at y==AC to anterior point (AP) along the y axis
- Item 2 PC: Distance from x-z-plane at y==AC to posterior commissure (PC) along the y axis
- Item 3 PP: Distance from x-z-plane at y==AC to posterior point (PP) along the y axis
- Item 4 SP: Distance from x-y-plane at z==AC to superior point (SP) along the z axis
- Item 5 IP: Distance from x-y-plane at z==AC to inferior point (IP) along the z axis
- Item 6 RP: Distance from y-z-plane at x==AC to right point (RP) along the x axis
- Item 7 LP: Distance from y-z-plane at x==AC to left point (LP) along the x axis
Example file content:
66.885850 26.500000 102.697017 68.035304 40.421205 65.232346 64.500000
Using these points, the transformation is then performed as shown in the figure and example below.
The default values are as such (all distances in mm):
Distance AC to AP 70 Distance AC to PC 23 Distance AC to PP 102 Distance AC to SP 74 Distance AC to IP 42 Distance AC to RP 68 Distance AC to LP 68
Example of how to apply Talairach values. The principle is followed in all three directions (x, y, z). First the compartment is identified (e.g. for z axis, superior to AC, or inferior to AC). Then the coordinate is scaled with the Talairach value divided by the real value.
For the posterior compartments (y-axis), it is slightly more complicated because there are two posterior compartments: Between AC and PC, and between PC and PP. Once it is decided which compartment is the correct one, the scaling is done for this compartment only; e.g. if the compartment is between PC and PP: First subtract the relevant points from the value, i.e. |y|’ = |y|-PC. Then, scale y’ with (PP_tal-PC_tal)/(PP-PC). Then add PC_tal. Done!